This example demonstrates multi-byte communication from the Arduino board to the computer using a call-and-response (handshaking) method.
This sketch sends an ASCII A (byte of value 65) on startup and repeats that until it gets a serial response from the computer. Then it sends three sensor values as single bytes, and waits for another response from the computer.
You can use the Arduino Software (IDE) serial monitor to view the sent data, or it can be read by Processing (see code below), Flash, PD, Max/MSP (see example below), etc.
Step 1: What You Need?
1 x Arduino Board ( Arduino UNO R3 used in this tutorial.)
2 x Analog Sensor ( Potentiometer, Photocell, etc.)
1 x Pushbutton
3 x 10k Ohm Resistors
1 x Mini Breadboard
1 x USB Type-B Cable
Male-to-Male Jumper Wires
Software Required
Optional
Don't have components? Don't worry. Just click the component's name. 2 x Analog Sensor ( Potentiometer, Photocell, etc.)
1 x Pushbutton
3 x 10k Ohm Resistors
1 x Mini Breadboard
1 x USB Type-B Cable
Male-to-Male Jumper Wires
Software Required
Optional
Step 2: Build Your Circuit.
Step 3: Upload The Code.
2. Find the port number by accessing device manager on Windows. See the section Port (COM&LPT) and look for an open port named "Arduino Uno (COMxx)". If you are using a different board, you will find a name accordingly. What matters is the xx in COMxx part. In my case, it's COM3. So my port number is 3.
Select the right port: Tools >> Port >> Select the port number.
3. You can find this code in the example of Arduino IDE.
Select File >> Examples >> 04.Communication >> SerialCallResponse
Click press the "upload" button (see the button with right arrow mark).
Processing Code
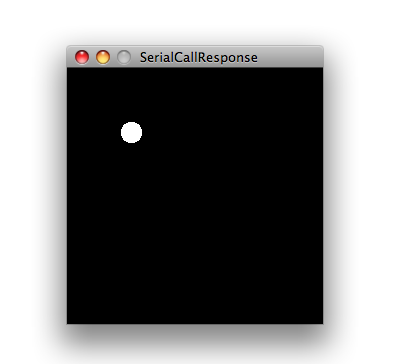
Copy the Processing sketch from the code sample above. As you change the value of the analog sensor, you'll get a ball moving onscreen something like this. The ball will appear only when you push the button:
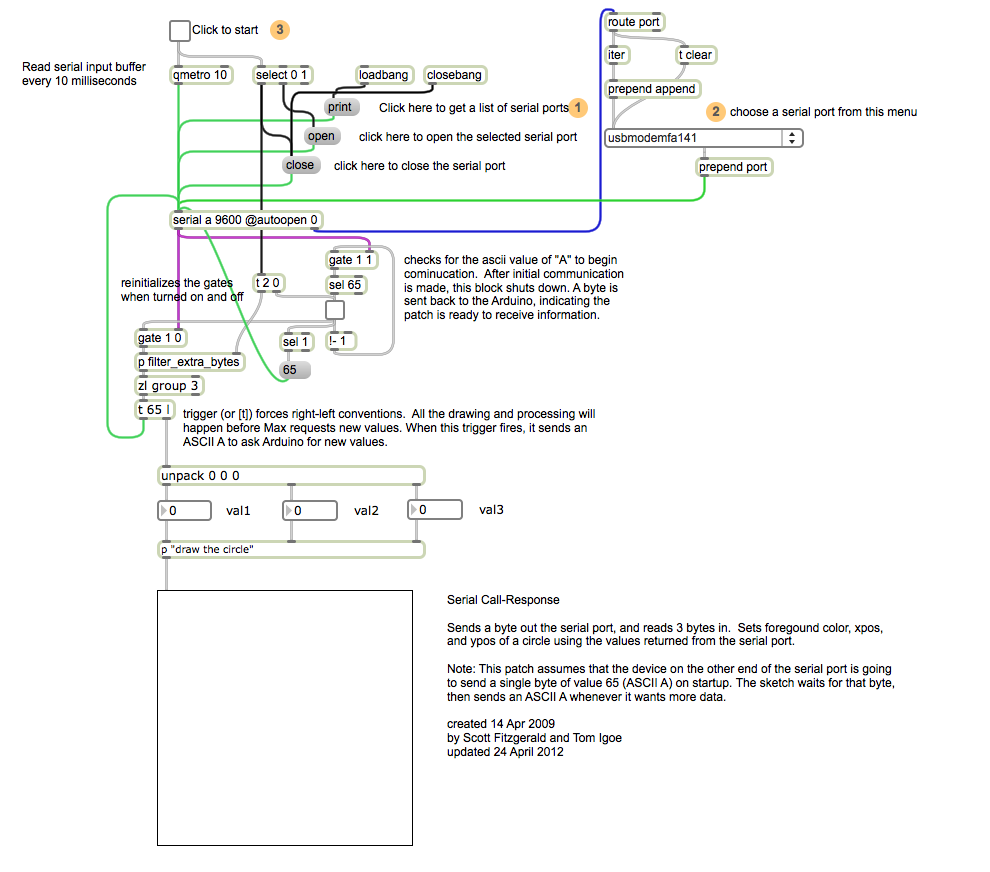
Max Code
The max patch looks like this. Copy the text from the code sample above.
Download:











0 comments:
Post a Comment